Power Industry

The power industry is a cornerstone of modern infrastructure, generating and distributing energy to meet global demands. Membrane technology plays a critical role in this sector, particularly in water and wastewater treatment processes essential for power plant operations. High-purity water is vital for steam generation in thermal and nuclear power plants to prevent scaling and corrosion in boilers and turbines.
Relevant Technologies
In the power industry, our expertise lies in membrane technologies that ensure efficient operations, particularly in water treatment, desalination, and wastewater management. These technologies help optimize water usage, reduce energy consumption, and support sustainable practices in power generation. Advanced systems such as membrane bioreactors (MBRs) support waste minimization and resource recovery, aligning with the industry’s commitment to environmental compliance and sustainability.
The typical processes involved are Pretreatment + Ultrafiltration + Reverse Osmosis, with parameters specifically set to ensure optimal water quality.
Ceramic Membranes
Ceramic membranes offer high durability and resistance to high temperatures and aggressive chemicals. MF membranes have the largest pore size among filtration membranes. Ultrafiltration (UF) membranes enable the separation of suspended solids, bacteria, and large molecules, while allowing smaller molecules like water and salts to pass through. They are commonly used as a pretreatment step before reverse osmosis (RO) systems to remove larger particles, reducing fouling and improving RO efficiency. Other applications include pretreatment for reverse osmosis, cooling water filtration, and wastewater treatment.
Spiral Wound Nanoflo®️ Membranes
Spiral Wound Nanoflo®️ technology is used for selective filtration of divalent ions and organic molecules. They are often employed when there is a need for softening water (removal of calcium and magnesium) or removing organic contaminants, without the need for full desalination.
Spiral Wound Reverse Osmosis (RO) Membranes
Spiral Wound Reverse Osmosis (RO) technology are used for desalination and water purification. They remove dissolved salts, minerals, and contaminants from feedwater, providing high-purity water essential for steam generation and cooling systems in power plants. RO is critical for achieving the required water quality in both thermal and nuclear power plants.
Membrane Bioreactors (MBRs)
MBR systems combine biological treatment with membrane filtration, typically using ultrafiltration (UF) membrane. These systems are widely used for wastewater treatment, effectively removing organic pollutants and suspended solids. The membrane filters separate treated water from biological sludge, ensuring the production of high-quality effluent. Applications include wastewater treatment and the recovery of resources from power plant effluents, promoting sustainability and resource conservation.
Electrodialysis (ED) and Electrodialysis Reversal (EDR)
Electrodialysis (ED) and Electrodialysis Reversal (EDR) use electric fields to drive the movement of ions through ion-exchange membranes, facilitating desalination and the removal of specific ions from water. Electrodialysis Reversal (EDR) is commonly used for brine management and can reduce chemical usage in the treatment process. Applications include the desalination of brackish water, demineralization of water, and treatment of power plant effluents, supporting both water quality improvement and environmental sustainability.
Nuclear Power Plant

In the nuclear power industry, membrane technology plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity and efficiency of plant operations. High-purity water is essential for cooling and steam generation in nuclear reactors, where impurities can lead to scaling, corrosion, and reduced efficiency.
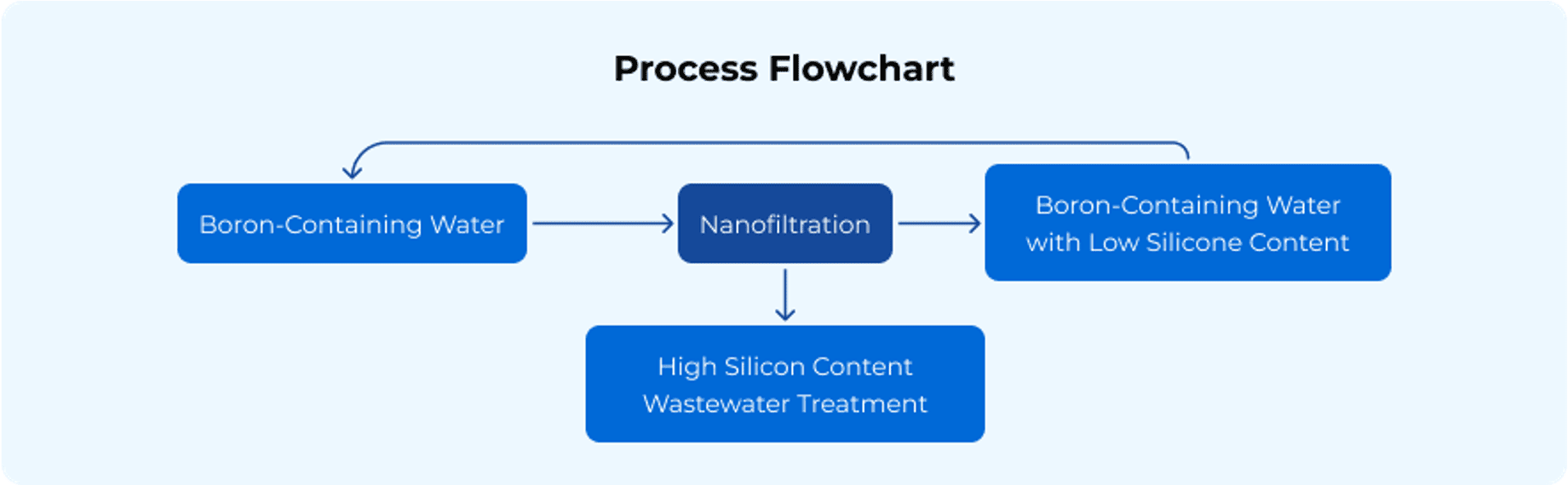
Nuclear power plants require strict control of dissolved silicon content in the boron-containing water systems of the primary circuit. When the silicon content exceeds the safety limit, the water system must be purified to reduce silicon concentration to ensure the safe operation of the units. However, the chemical and physical properties of dissolved silicon are very similar to those of boric acid, making separation challenging.
Due to the stringent water quality requirements in nuclear power plants, no additional impurities can be introduced during the removal process. Additionally, it is crucial to maintain a high recovery rate of boric acid and minimize the generation of waste.
Process Flowchart
Relevant Technologies
Our expertise lies in membrane technologies designed to purify water, remove dissolved salts, and prevent contaminants from entering cooling systems and boilers. Membrane bioreactors (MBRs) effectively treat wastewater generated within the plant, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations and reducing pollutant discharge. By enhancing water quality, membrane technology plays a vital role in supporting the safe, efficient, and environmentally responsible operation of nuclear plants.
The implementation of membrane technologies enables nuclear plants to improve operational efficiency, reduce costs, and minimize environmental impact, contributing to greater sustainability and safety within the industry.
Ceramic Ultrafiltration (UF) Membranes
Ceramic Ultrafiltration (UF) technology is used to remove particulate matter and larger molecules from water sources to meet strict quality requirements.
Spiral Wound Nanoflo®️ Membranes
Nuclear plants require highly purified water for cooling and steam generation. Spiral Wound Nanoflo®️ Membrane technology is utilized to remove salts, ions, and impurities, ensuring that only the cleanest water is used in reactors and cooling systems. Additionally, nanofiltration effectively reduces silicon concentration in the boron-containing water system to a safe level (<500 ppb), while minimizing waste discharge and maintaining stable boron concentrations within the system.
Spiral Wound Reverse Osmosis (RO) Membranes
Spiral Wound Reverse Osmosis (RO) technology is a membrane-based desalination technology, used in nuclear power plants located in coastal areas to produce fresh water from seawater. This water can be used for cooling, cleaning, and other operations within the plant. RO technology is ideal for removing radioactive elements and other contaminants, ensuring the safe and environmentally responsible management of wastewater in nuclear power plants
Membrane Bioreactors (MBRs)
Nuclear power plants generate significant amounts of wastewater from various operations, including cooling, maintenance, and decommissioning activities. Membrane bioreactor (MBR) systems are essential for treating this wastewater, making it suitable for reuse within the plant or for safe disposal without harming the environment. MBRs are particularly effective in treating organic-rich waste streams, ensuring that the wastewater is properly treated before reuse or disposal.
Fermentation

The fermentation industry produces wastewater as a byproduct at various stages of the production process, where raw materials such as sugars and starches are microbially converted into valuable products like ethanol, organic acids, enzymes, and antibiotics.
Wastewater is generated during multiple operations, including raw material washing, fermentation, product recovery, equipment cleaning, and utility usage. This effluent is typically high in biochemical and chemical oxygen demand (BOD/COD), suspended solids, residual sugars, alcohols, organic acids, and cleaning agents from CIP (cleaning-in-place) systems. It may also contain significant levels of nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus, making it difficult to treat and unsuitable for direct discharge or reuse without proper treatment.
Relevant Technologies
Our expertise lies in membrane technologies designed to purify water, remove dissolved salts, and prevent contaminants from entering cooling systems and boilers. Membrane bioreactors (MBRs) effectively treat wastewater generated within the plant, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations and reducing pollutant discharge. By enhancing water quality, membrane technology plays a vital role in supporting the safe, efficient, and environmentally responsible operation of nuclear plants.
Hollow Fiber Ultrafiltration (UF) Membranes
Hollow Fiber Ultrafiltration (UF) technology can be used for both pretreatment and final polishing by effectively removing suspended solids and stabilizing the treatment process. As a pretreatment step before biological systems, hollow fiber UF removes suspended solids, biomass residues, and high-load particulates that could otherwise overload the biological units. This enhances overall treatment stability and reduces maintenance requirements for downstream processes.
Spiral Wound Nanoflo®️ Membranes
In certain fermentation processes, wastewater may still contain residual sugars, organic acids, or other valuable compounds. Spiral Wound Nanoflo®️ Membranes can concentrate these substances for potential recovery, while allowing water and smaller salts to pass through. This not only reduces waste but also enhances value through resource recovery.
Spiral Wound Reverse Osmosis (RO) Membranes
Spiral Wound Reverse osmosis (RO) membranes can serve as a final polishing step to meet stringent discharge regulations or to prepare water for reuse within the plant. RO treated water can be reused for clean-in-place (CIP) systems, cooling towers, or even as process water, provided the quality meets requirements, thereby reducing dependence on freshwater sources. This is particularly valuable in water-scarce regions or for industries pursuing zero liquid discharge (ZLD) goals.
Membrane Bioreactors (MBRs)
Membrane Bioreactors (MBRs) offering an efficient and compact solution for treating high-strength wastewater. They combine biological degradation of organic pollutants with membrane filtration to effectively separate biomass and suspended solids, producing high-quality effluent. This technology can handle fluctuations in wastewater composition and load typical of fermentation processes, reduce sludge production, and eliminate the need for large settling tanks.
MBRs provide better control of inhibitory by-products in the wastewater, helping maintain stable conditions within the fermentation system. The treated water can be directly discharged or further processed using nanofiltration (NF) or reverse osmosis (RO) membranes for reuse, supporting initiatives to reduce freshwater consumption and minimise environmental impact.
Leather

The leather industry heavily relies on water intensive processes such as soaking, tanning, dyeing, and finishing, which generate significant amounts of wastewater laden with organic matter, salts, and heavy metals. Membrane technology has emerged as an effective solution for wastewater treatment and resource recovery in the leather industry. The typical processes involved are Pretreatment + Ultrafiltration + Reverse Osmosis, with parameters specifically set to ensure optimal water quality.
Relevant Technologies
Our expertise lies in membrane technologies designed to purify water, remove dissolved salts, and prevent contaminants from entering cooling systems and boilers. Membrane bioreactors (MBRs) effectively treat wastewater generated within the plant, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations and reducing pollutant discharge. By enhancing water quality, membrane technology plays a vital role in supporting the safe, efficient, and environmentally responsible operation of nuclear plants.
Ceramic Microfiltration (MF) Membranes
Ceramic Microfiltration (MF) technology is often used as a pre-treatment step. Microfiltration membranes filter out larger particles and microorganisms, thereby protecting downstream processes like UF and RO and and ensuring better water quality for further treatment stages.
Hollow Fiber Ultrafiltration (UF) Membranes
Hollow Fiber Ultrafiltration (UF) technology is used to remove larger organic molecules, colloids, and suspended solids from the wastewater, making it suitable for further processing.
Spiral Wound Nanoflo®️ Membranes
Spiral Wound Nanoflo®️ technology effectively removes dissolved salts, organic acids, and small molecules. It concentrates and recycles tanning chemicals, reducing the need for fresh chemicals and minimizing waste.
Spiral Wound Reverse Osmosis (RO) Membranes
Spiral Wound Reverse osmosis (RO) technology crucial for removing dissolved salts, organic matter, and other small pollutants, producing high-quality water that can be reused in leather production processes.
Membrane Bioreactors (MBRs)
Membrane bioreactors (MBR) combine biological treatment with membrane filtration, offering an integrated solution for treating tannery wastewater. MBR systems effectively eliminate organic and inorganic pollutants, producing high-quality effluent suitable for reuse or safe discharge. This process significantly enhances the overall water treatment and sustainability in the leather industry.
Rare Earth Mining

Rare earth mining involves extracting a group of 17 chemical elements known as rare earth elements (REEs) from the earth’s crust. These elements are crucial for various high-tech applications, including electronics, renewable energy technologies, and advanced materials. Traditional mining methods often have significant environmental impacts, such as generating hazardous waste and depleting natural resources. To mitigate these issues, membrane technology is increasingly being used in rare earth element extraction. This technology employs selective barriers to separate valuable rare earth elements from waste materials more efficiently and with less environmental impact. Membrane processes can reduce the need for harmful chemicals and lower energy consumption, making the extraction process greener and more sustainable.
Relevant Technologies
Water from rare earth element extraction is treated through pretreatment such as sedimentation, MMF or biological treatment such as AO MBR. By using microorganisms such as nitrifying bacteria and denitrifying bacteria, this system can achieve high levels of oxygen removal.
The typical processes involved are Pretreatment + Ultrafiltration + Reverse Osmosis, with parameters specifically set to ensure optimal water quality.
Ceramic Microfiltration (MF) Membranes
In rare earth mining, microfiltration technology can be used in the initial stages of processing. It helps in removing larger particulates and suspended solids from the mining slurry, ensuring that the downstream processes deal with a cleaner feed. This step is crucial for protecting and enhancing the efficiency of subsequent membrane processes.
Hollow Fiber Ultrafiltration (UF) Membranes
Ultrafiltration is typically used to further purify the slurry after microfiltration. It can remove smaller particles and organic matter that microfiltration might miss. In the context of rare earth mining, UF can help in concentrating rare earth elements by filtering out unwanted larger molecules, leaving a more concentrated solution of REEs.
Spiral Wound Nanoflo®️ Membranes
Spiral Wound Nanoflo®️ technology are more selective and can be used to separate specific rare earth ions from the mixture. This technology is particularly beneficial for isolating rare earth elements from complex mixtures, as it can reject multi-valent ions and small organic molecules while allowing monovalent salts to pass through. This makes NF effective for selectively concentrating on specific rare earth elements.
Spiral Wound Reverse Osmosis (RO) Membranes
Spiral Wound Reverse Osmosis (RO) technology is highly effective for the final concentration and purification of rare earth elements. It can remove nearly all dissolved solids, including a wide range of ions and small organic compounds. In rare earth mining, RO can be used to achieve very high purity levels of the final product, ensuring that the extracted rare earth elements meet the required standards for high-tech applications.
Steel

In the steel industry, membrane technology plays a crucial role in improving environmental sustainability and process efficiency. Membrane technology are employed to treat and recycle wastewater generated during various production stages, such as cooling, pickling, and rinsing. This not only reduces freshwater consumption and wastewater discharge but also helps maintain regulatory compliance.
Relevant Technologies
Our expertise lies in multimedia filtration and reverse osmosis to effectively remove contaminants, enabling the reuse of water within the plant. The typical processes involved are pretreatment, ultrafiltration, and reverse osmosis, with parameters specifically set to ensure optimal water quality.
Ceramic Microfiltration (MF) Membranes
Used as a pre-treatment step, this membrane filters out larger particles and microorganisms, protecting subsequent membrane processes.
Hollow Fiber Ultrafiltration (UF) Membranes
Ultrafiltration (UF) technology eliminates suspended solids, colloids, and larger organic molecules, preparing water for further purification steps.
Spiral Wound Nanoflo®️ Membranes
Spiral Wound Nanoflo®️ Membranes technology allows certain salts to pass through while removing larger organic molecules and multivalent ions, ensuring water meets specific reuse criteria.
Spiral Wound Reverse Osmosis (RO) Membranes
Spiral Wound Reverse Osmosis (RO) technology removes dissolved salts, heavy metals, and other small pollutants, resulting in high-quality water suitable for reuse in various stages of steel production.
Membrane Bioreactors (MBRs)
Combining biological treatment with membrane filtration, membrane bioreactors effectively eliminate organic and inorganic pollutants from wastewater, enhancing the overall treatment process and making the water suitable for recycling.
Petrochemical

Suntar’s EGSB Plus Systems offers several advantages over conventional methods:
- Compact footprint
- Uniform Feed Water Distribution
- Elimination of stagnant water zones within the reactors
- Enhanced mass transfer efficiency
Process Flowchart

Relevant Technologies
Anaerobic Treatment
Primary Biological COD Reduction
- PTA wastewater contains high levels of COD from residual acetic acid, benzoic acid, p-xylene, and other organics.
- EGSB Plus removes up to 70 – 90% of COD by converting organics into biogas. The robust biogas production from EGSB Plus – suitable for power generation and substantially reduces operational costs.
Handles High Loading Rates Efficiently
EGSB Plus is designed for high volumetric loading rates and compact footprint, ideal for petrochemical plants with large wastewater volumes and space constraints.
Minimal Sludge Loss
Prepares for Aerobic/Post-Treatment
- After anaerobic digestion, effluent is still rich in some biodegradable compounds and nutrients.
- The EGSB Plus effluent typically goes to aerobic treatment (e.g., activated sludge or MBR) to meet final discharge or reuse standards.
- In aerobic treatment, Suntar’s Jet Aerators leverage a specialised jet arm guide ring and air distribution chamber design to create high negative pressure and intense turbulence when the wastewater and the air mix in the aerators. This generates smaller but more bubbles with increased total surface area and reduces mass transfer resistance, boosting oxygenation efficiency.
Pressurised Ultrafiltration (UF) Membranes
Spiral Wound Reverse Osmosis (RO) Membranes
Oilfield

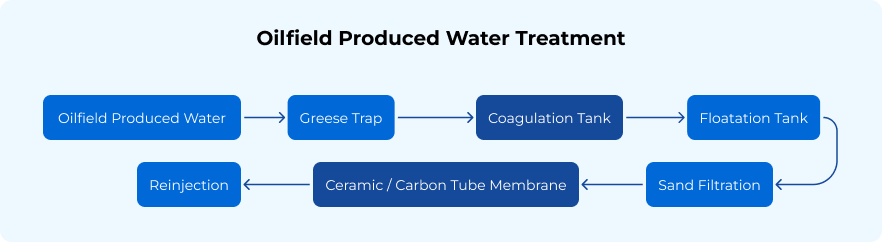
The oil-field industry plays a pivotal role in global energy production, involving the exploration, extraction, and processing of crude oil and natural gas. This industry employs advanced technologies and techniques, such as drilling, hydraulic fracturing, and enhanced oil recovery, to efficiently access and extract hydrocarbons from underground reservoirs. The industry is increasingly focusing on sustainability, with efforts to reduce environmental impact through improved water management, waste treatment, and the adoption of greener practices. Membrane technology is used to treat and recycle produced water, helping to minimize wastewater discharge and reduce the industry’s overall environmental footprint.
Process Flowchart

Relevant Technologies
Membrane technologies have become essential in the oilfield industry due to their efficiency in treating produced water, brine, and other waste streams. The typical processes involved are Pretreatment + Ultrafiltration + Reverse Osmosis, with parameters specifically set to ensure optimal water quality.
Ceramic Microfiltration (MF) Membranes
Ceramic Microfiltration (MF) technology offers robust, high-temperature, and chemical-resistant solutions for oil-water separation. It efficiently separates free and emulsified oil under extreme temperature and pressure conditions, enabling the recovery of valuable hydrocarbons from wastewater streams and reducing waste.
Hollow Fiber Ultrafiltration (UF) Membranes
Hollow Fiber Ultrafiltration (UF) technology is effective in removing suspended solids from produced water.
Spiral Wound Nanoflo®️ Membranes
Spiral Wound Nanoflo®️ technology allows partial desalination of water for Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR) for selective removal of divalent and trivalent ions.
Spiral Wound Reverse Osmosis (RO) Membranes
Spiral Wound Reverse Osmosis (RO) technology crucial for removing salts and dissolved solids to produce low-salinity water for EOR applications.
Metallurgy

The metallurgy industry is integral to extracting, refining, and processing metals essential for construction, manufacturing, transportation, and technology. Membrane technology has emerged as a key enabler of sustainable and efficient practices in this sector. It enables the treatment and recycling of wastewater, recovery of valuable metals, and removal of impurities. These innovations not only reduce freshwater consumption and waste discharge but also ensure compliance with environmental standards, enhancing overall resource efficiency and supporting sustainable metallurgical operations.
Relevant Technologies
Our membrane systems are designed to efficiently recover valuable metals from industrial effluents and processing streams. By utilizing advanced membrane technology, these systems enable the recovery and purification of acids and alkalis from metallurgical waste streams, significantly reducing chemical consumption and operational costs. Additionally, our solutions effectively treat effluents containing heavy metals, acids, and organic contaminants, ensuring compliance with stringent environmental discharge standards. The typical processes involved are Pretreatment + Ultrafiltration + Reverse Osmosis, with parameters specifically set to ensure optimal water quality.
Hollow Fiber Ultrafiltration (UF) Membranes
Hollow Fiber Ultrafiltration (UF) technology effectively removes suspended solids, emulsified oils, and particulate matter from wastewater, ensuring high-quality treatment and improved water reuse potential.
Spiral Wound Nanoflo®️ Membranes
For metal recovery and recycling, Spiral Wound Nanoflo®️ Membranes technology is used to separate and concentrate heavy metals such as copper, nickel, and zinc from wastewater. In water and wastewater treatment, it effectively separates dissolved salts and heavy metals from water streams, contributing to efficient resource recovery and cleaner effluent.
Spiral Wound Reverse Osmosis (RO) Membrane
For metal recovery and recycling, Spiral Wound Reverse Osmosis (RO) technology recovers high-purity water and concentrates metal solutions for reuse or further processing. In water and wastewater treatment, it effectively separates dissolved salts and heavy metals from water streams, enhancing resource efficiency and environmental sustainability
Electrodialysis (ED)
For metal recovery and recycling, electrodialysis (ED) separates and recovers ionic metals from electrolytic solutions. In acid and alkali recovery, it efficiently recovers acids (e.g., sulfuric acid) and alkalis from pickling baths and other waste streams, contributing to resource conservation and reducing waste.
Membrane Bioreactors (MBRs)
Combining biological treatment with membrane filtration, membrane bioreactors effectively eliminate organic and inorganic pollutants from wastewater, enhancing the overall treatment process and making the water suitable for recycling.
Pulp and Paper

The pulp and paper industry is a key sector that produces paper, cardboard, and other paper-based products, relying heavily on use of water in various stages of production. This process generates large volumes of wastewater, often containing high levels of organic materials, fibers, and chemicals. Membrane technology plays a vital role in addressing environmental concerns by efficiently treating this wastewater.
Relevant Technologies
Membrane filtration methods, such as ultrafiltration (UF) and reverse osmosis (RO), help in the removal of suspended solids, color, and harmful chemicals, enabling water recycling and reducing the environmental footprint. Additionally, membrane systems aid in improving process efficiency, reducing chemical usage, and enhancing overall sustainability in the pulp and paper industry.
The typical processes involved are Pretreatment + Ultrafiltration + Reverse Osmosis, with parameters specifically set to ensure optimal water quality.
Ceramic Microfiltration (MF) Membranes
Ceramic Microfiltration (MF) technology is used in the initial stages of wastewater treatment to remove larger particles and bacteria. It can help in reducing the overall load on other treatment processes like UF or RO.
Hollow Fiber Ultrafiltration (UF) Membranes
Hollow Fiber Ultrafiltration (UF) technology eliminates suspended solids, colloidal particles, and some dissolved materials from the wastewater. UF technology is effective at clarifying water, reducing the load on downstream processes like biological treatment, and enabling the reuse of water in various stages of paper production.
Spiral Wound Nanoflo®️ Membranes
Spiral Wound NF technology operates between UF and RO in terms of pore size and removal capability. It is used to remove divalent ions, organic matter, and some dissolved solids from water, offering a balance between filtration efficiency and energy consumption
Spiral Wound Reverse Osmosis (RO) Membranes
Spiral Wound Reverse Osmosis (RO) technology is used for more advanced water treatment, particularly for removing dissolved salts, organic contaminants, and chemicals from the water. RO technology provides high-quality permeation, making it suitable for recycling water in processes that require very low concentrations of contaminants.
Coal-Chemical

The coal-chemical industry involves the conversion of coal into various chemicals, such as fertilizers, synthetic fuels, and petrochemical products. This industry faces significant challenges in terms of resource efficiency, environmental impact, and waste management. Membrane technology plays a crucial role in addressing these challenges by providing efficient separation processes for water purification, desalination, and the recovery of valuable by-products. Membrane technology, including ultrafiltration, reverse osmosis, and nanofiltration, are increasingly used to improve the treatment of wastewater, reduce chemical consumption, and enhance overall sustainability in coal-chemical plants.
Relevant Technologies
Membrane filtration methods, such as ultrafiltration (UF) and reverse osmosis (RO), help in the removal of suspended solids, color, and harmful chemicals, enabling water recycling and reducing the environmental footprint. Additionally, membrane systems aid in improving process efficiency, reducing chemical usage, and enhancing overall sustainability in the pulp and paper industry.
The typical processes involved are Pretreatment + Ultrafiltration + Reverse Osmosis, with parameters specifically set to ensure optimal water quality.
Hollow Fiber Ultrafiltration (UF) Membranes
Hollow Fiber Ultrafiltration (UF) technology is used to separate fine particles, organic matter, and colloidal substances from water and wastewater. It is applied in the pre-treatment of water and the recycling of processed water, helping to reduce water consumption and ensure better water quality for reuse.
Spiral Wound Nanoflo®️ Membranes
Spiral Wound Nanoflo®️ technology is employed for the selective separation of divalent ions and small organic molecules. This is particularly useful in wastewater treatment, effectively removing contaminants such as sulfate, hardness, and organic substances.
Spiral Wound Reverse Osmosis (RO) Membranes
Spiral Wound Reverse Osmosis (RO) technology is used to desalinate and purify water, especially in processes that require high-quality water, such as cooling systems or the production of synthetic fuels and chemicals. It effectively removes salts, heavy metals, and other impurities from water sources, ensuring clean and reliable water for various applications.
Membrane Bioreactors (MBRs)
MBR systems combine biological treatment with membrane filtration. They are used in wastewater treatment to improve the removal of organic and inorganic contaminants, reducing the footprint of treatment plants while enhancing effluent quality.
Electrodialysis (ED)
In certain processes, electrodialysis membranes are used for selective ion removal and to treat brine streams, allowing for the recovery of valuable chemicals and minimizing waste disposal.
Oil-Water Separation

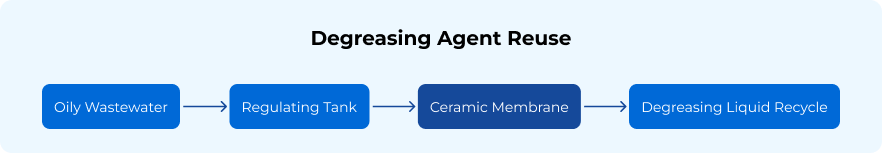
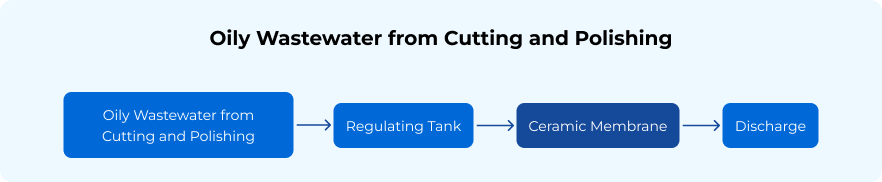
The oil-water separation process plays a crucial role in environmental protection by removing oil and other contaminants from water across various sectors, including oil and gas, petrochemicals, and wastewater treatment. Oilfield wastewater is complex, containing petroleum, demulsifiers, salts, phenols, sulfur, and other pollutants harmful to the environment. The treatment of oil production effluent focuses on removing oil and suspended solids to prevent the reinjection of contaminated water into the oil field, which could block the oil production layer. Membrane technology enhances separation efficiency, reduces chemical usage, and enables the recycling of treated water, making the oil-water separation process more environmentally friendly and cost-effective.
Process Flowchart
Relevant Technologies
Our technology effectively addresses various water and wastewater challenges, including oilfield produced water, cold rolling oily wastewater, reuse of degreasing fluid, coking oil wastewater treatment, and oily wastewater from cutting and polishing. We provide advanced solutions for the treatment and recycling of these challenging effluents, ensuring efficient oil-water separation and sustainable water management across multiple industries.
Ceramic Microfiltration (MF) Membranes
Ceramic Microfiltration (MF) technology is used to remove coarse oil droplets and suspended solids, effectively separating emulsions and particulates from water in the initial stages of oil-water separation. The oily wastewater passes through the adjustment tank and is processed by ceramic membranes to meet discharge standards, eliminating the need for coagulation, air flotation, sand filtration, and other steps. This ensures cleaner water for downstream processes, improving efficiency and reducing treatment complexity.
Ceramic Ultrafiltration (UF) Membranes
Ceramic Ultrafiltration (UF) technology is effective in removing larger oil droplets, suspended solids, and other particulate matter from oil-water mixtures. This technology is commonly used in treating produced water from oil and gas operations or industrial wastewater, providing pre-treatment before further processing or discharge.
Spiral Wound Nanoflo®️ Membranes
Spiral Wound NF technology provides selective separation of divalent ions, small organic molecules, and emulsified oils. NF technology is used for further treatment of water after primary separation, improving the overall quality of the treated water.
Spiral Wound Reverse Osmosis (RO) Membranes
Spiral Wound Reverse Osmosis (RO) technology is employed in advanced oil-water separation processes to remove dissolved contaminants, such as salts, small organic molecules, and fine emulsions, from water. This process is particularly useful for achieving high-quality effluent or for desalination of water after the initial oil separation.
Electrodialysis (ED)
This process uses ion-exchange membranes to selectively separate ionic contaminants from water. In the context of oil-water separation, electrodialysis can be used to recover valuable chemicals from brine or remove ions that might interfere with oil separation.
